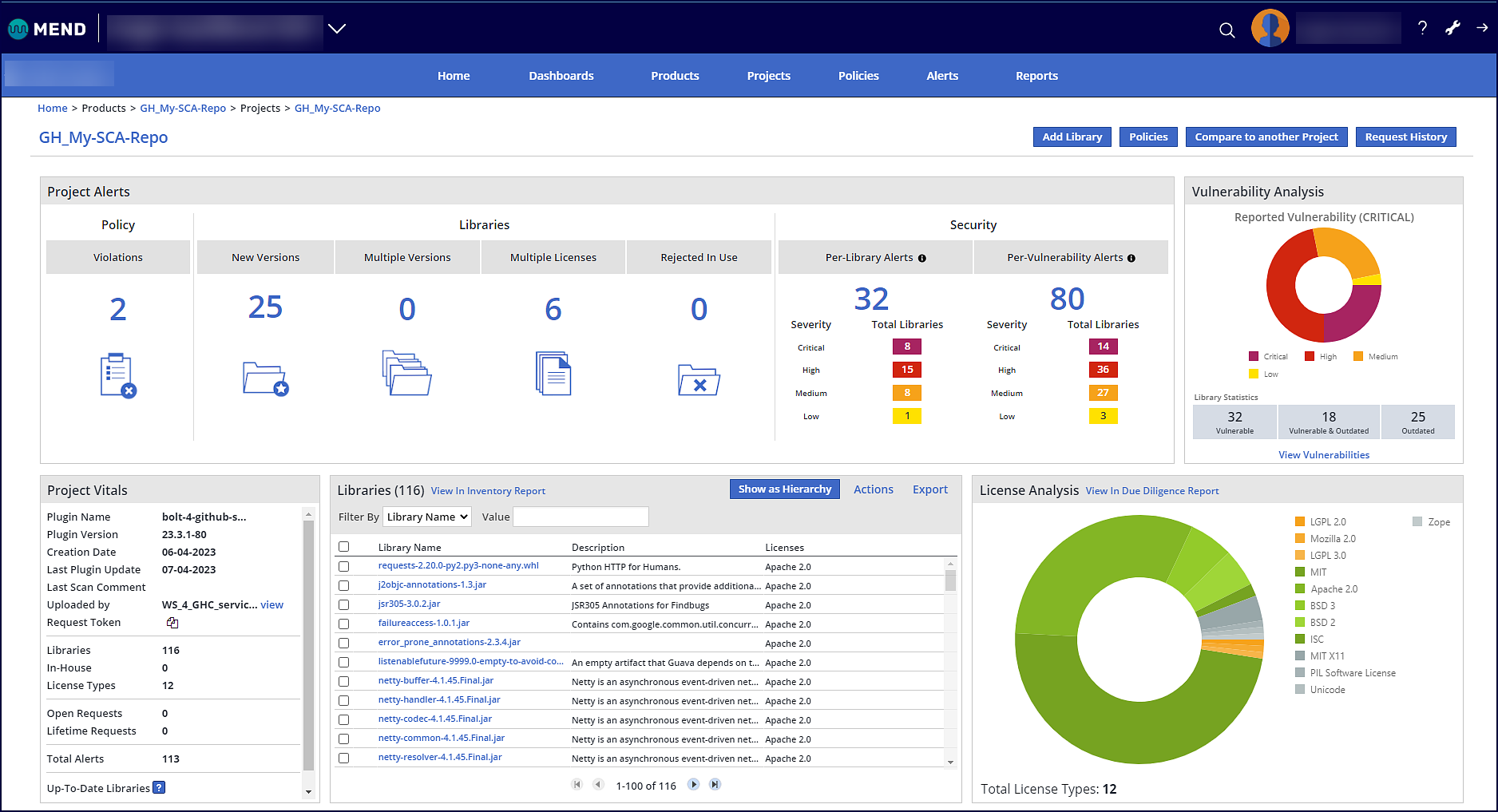
View the results of your Mend for GitHub.com SCA scan
Overview
Once your Mend for GitHub.com SCA scan is completed, there are multiple resources provided to help you review, analyze, and triage your results.
GitHub Check
Once the Mend for GitHub.com SCA scan is completed, the Mend checks are updated with the results. Both the Mend Security Check and the Mend License Check include a Scan token, which you can provide to Mend Support for troubleshooting.
Mend Security Check
The Security Report within the Mend Security Check populates within an overview of vulnerability findings within the commit:
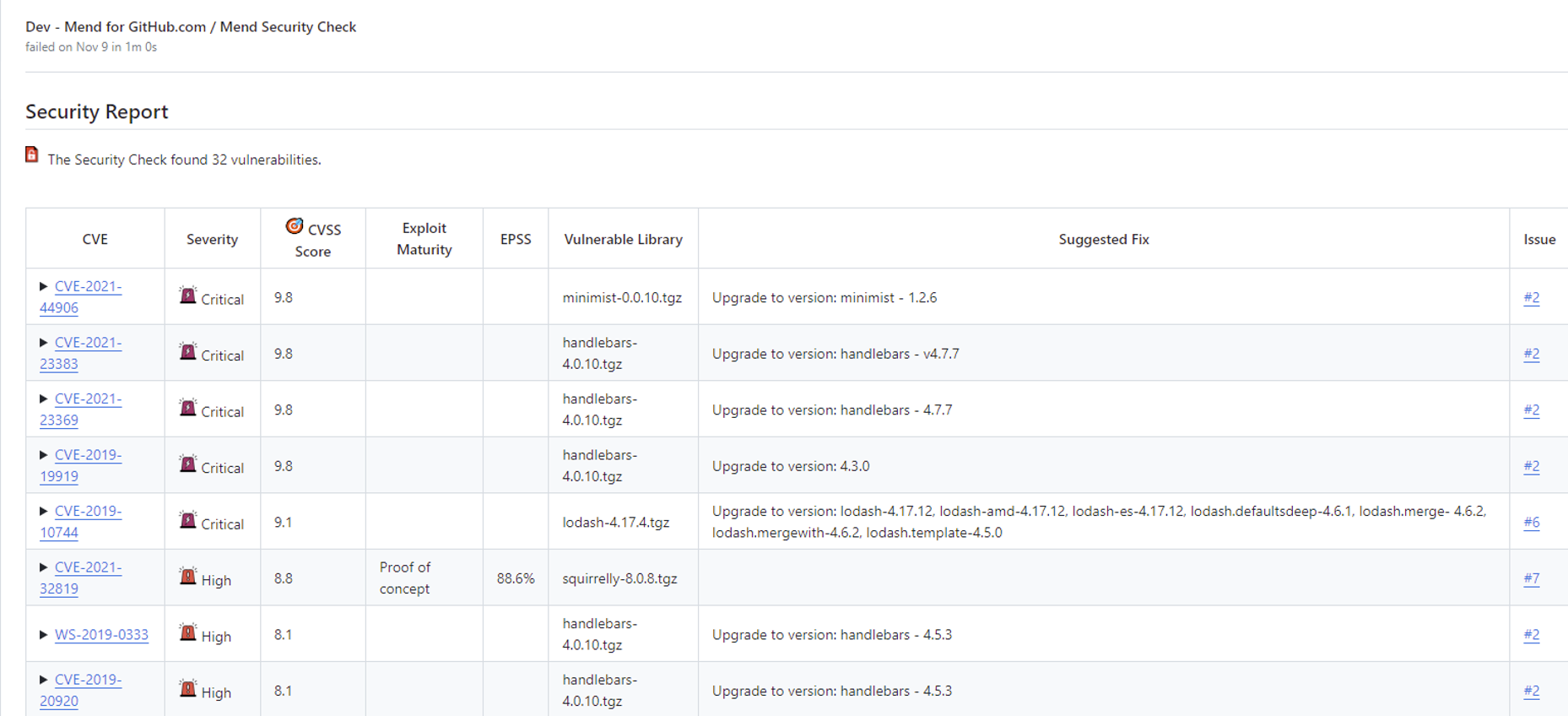
CVE: CVE ID of the vulnerability. This links to CVE’s page on Mend’s official database site.
Severity: Level of severity of the vulnerability (
Critical,High,Medium,Low)CVSS Score: CVSS Score (CVSS 3).
*Exploit Maturity: The Exploit Code Maturity (Proof of concept, Functional and High are reported by Mend as exploitable).
*EPSS: The EPSS percentage (probability of a vulnerability to be exploited)
Vulnerable Library: Name of the open-source component impacted by the vulnerability.
Suggested Fix: Fix suggestion to resolve the vulnerability.
Issue: URL to the related GitHub Issue that was created for the policy violation.
*Applicable when the exploitability flag is enabled, when a vulnerability contains exploitability data
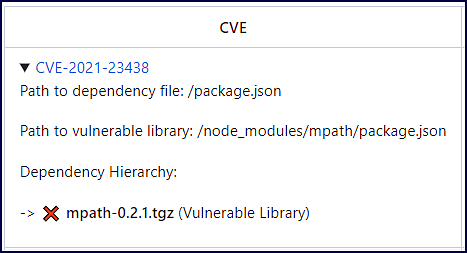
You can also click the dropdown arrow next to each CVE for more details:
Mend License Check
If you have the license violation analysis enabled as part of your SCA scan, the License Report within the Mend License Check will populate with any policy violation findings:
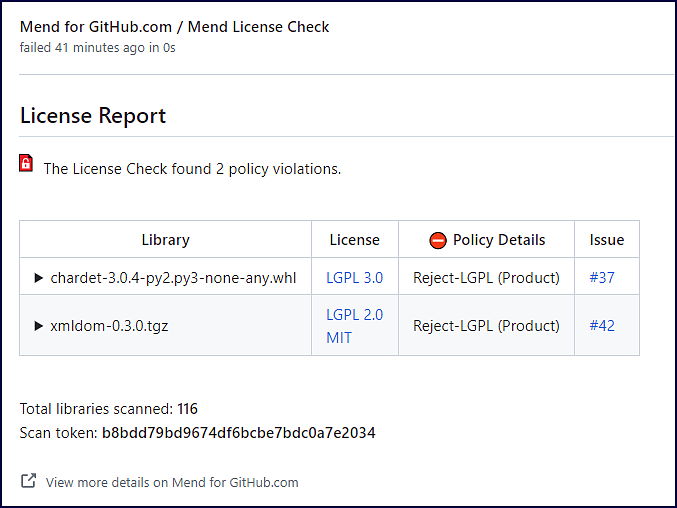
Library: Name of the open-source component impacted by the policy violation.
License: License type that was detected
Policy Details: Name of the license policy violation as defined in the Mend SCA UI, along with the policy level (Organization/Product/Project).
Issue: URL to the related GitHub Issue that was created for the policy violation.
You can also click the dropdown arrow next to each library for more details:
Mend Platform UI
Within the Mend Platform, an application is created for each repository with a “GH_" prefix. When a scan is completed for each branch defined in your baseBranches parameter, a project is created for that branch with a “GH_" prefix.
GitHub Issue
Once the Mend for GitHub.com SCA scan is completed, by default, the Mend SCA Check creates a GitHub Issue for the findings of each SCA component, if any were discovered.
Mend SCA Security Issue
Note: By default, each SCA Security Issue is created with the “Mend: dependency security vulnerability” Issue label.
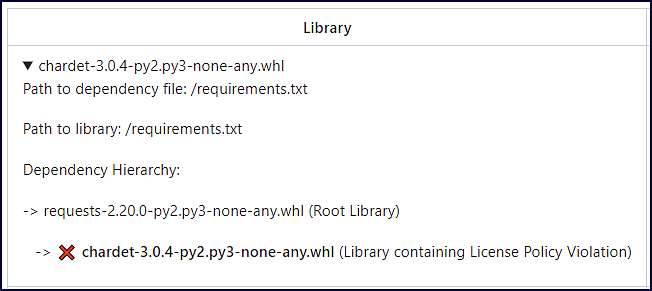
Component-based Library Security Issues

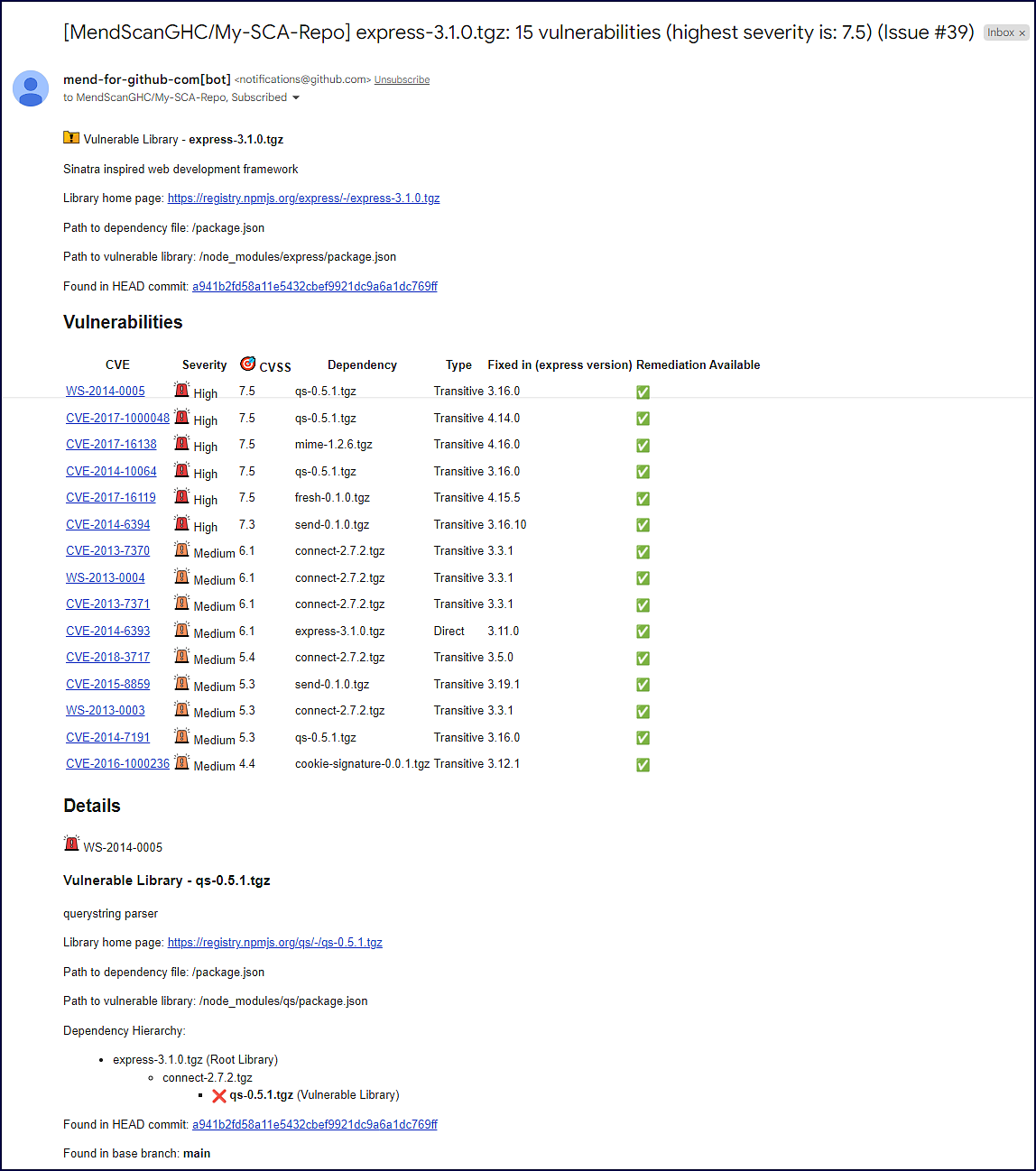
Vulnerable Library: Name of the vulnerable dependency file. Click on the dropdown arrow for more information. This information includes the path to the dependency file and the path of the library. If the path is of a transitive dependency, then only the path information of the root library is displayed. This section also contains a commit link, which includes the path to the commit link where the vulnerability was found.
Note: The originating branch of the vulnerability is also displayed in case the baseBranches configuration was used.
Vulnerabilities table:
CVE: CVE ID of the vulnerability. This links to CVE’s page on Mend’s official database site.
Severity: Level of severity of the vulnerability (
Critical,High,Medium,Low)CVSS: CVSS Score (CVSS 3).
*Exploit Maturity: The Exploit Code Maturity (Proof of concept, Functional and High are reported by Mend as exploitable).
*EPSS: The EPSS percentage (probability of a vulnerability to be exploited)
Dependency: Name of the dependency file.
Type: The type of dependency (
DirectorTransitive).Fixed in: Version of the dependency that fixes the vulnerability.
Remediation Available: If remediation is available (via Mend Remediate) there will be a green checkmark icon. If remediation is not available, there will be a red “X” icon.
*Applicable when the exploitability flag is enabled, when a vulnerability contains exploitability data
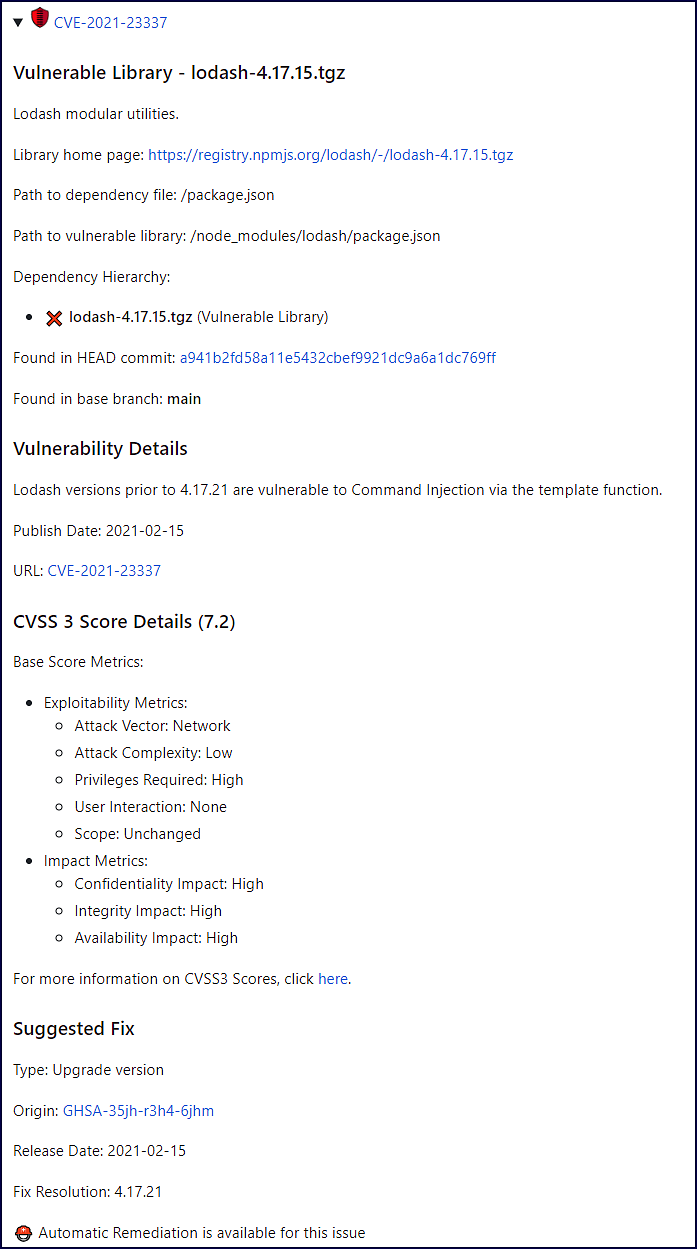
Details: List of CVEs found by the SCA scan on the open-source component. Click on each CVE’s dropdown arrow for a deep-dive on the CVE vulnerability and how it impacts the open-source component:
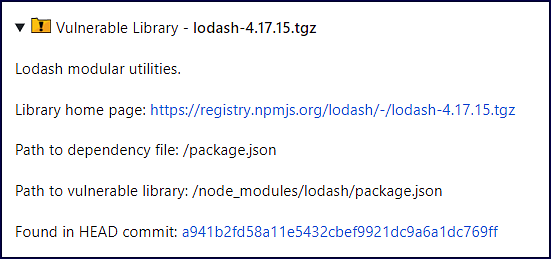
Source file-based component:
Note: By default, source file mapping for open-source components is disabled in Mend for GitHub.com.
Vulnerable library: Includes a description of the vulnerable source library, a link to the source library home page, a commit link, and the path to the commit link where the vulnerability was found. NOTE: The originating branch of the vulnerability is also displayed in case the baseBranches configuration was used.
Library Source Files - A list of source files found in the vulnerability source library.
Vulnerability Details: Description of vulnerability, published date, and link to the vulnerability source website.
CVSS 3 score: Basic CVSS3 score metrics. If this score is not available then the CVSS 2 score is displayed.
Suggested fix: A detailed suggestion that includes type, origin, release date, and fix resolution. Note that a fix may not always be available.
Mend License Violation Issue
Note: If you have the license violation analysis enabled as part of your SCA scan, the integration will create a GitHub Issue for each violation finding. By default, each License Violation Issue is created with the “Mend: license policy violation” Issue label.
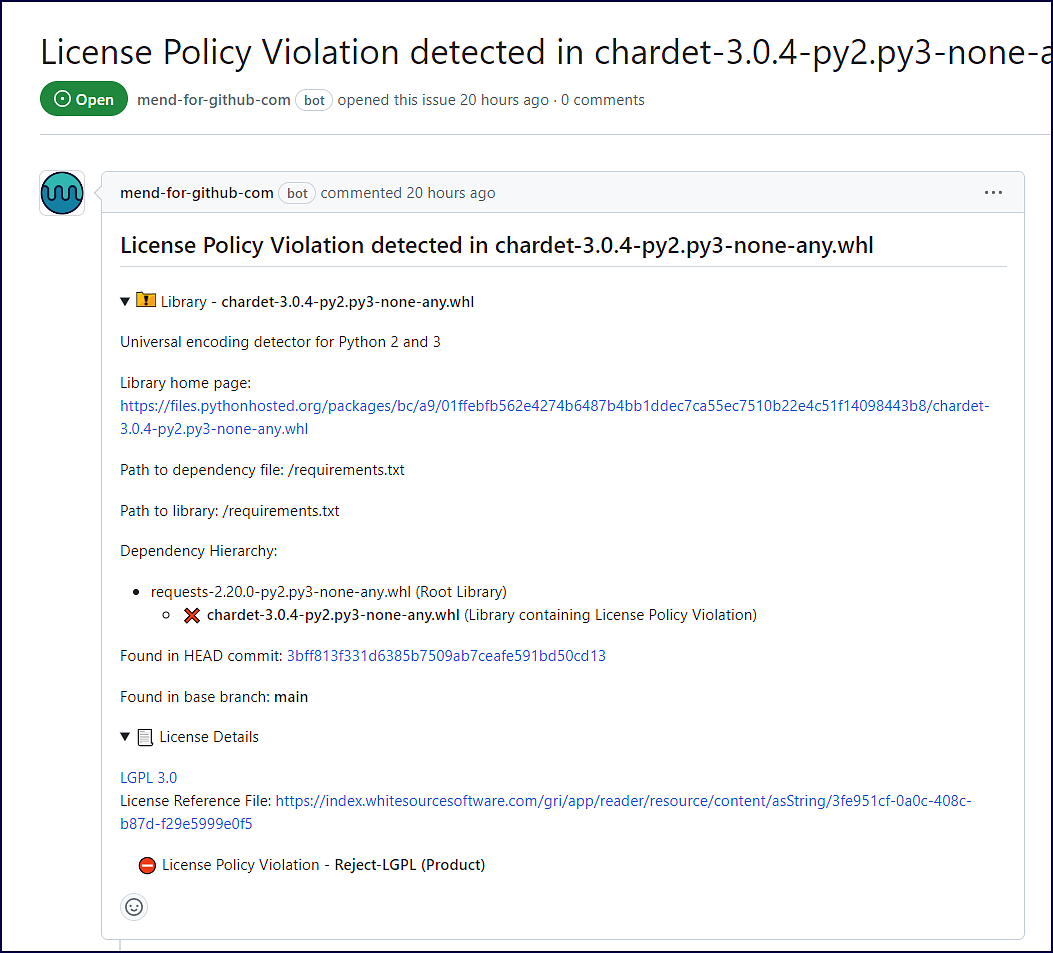
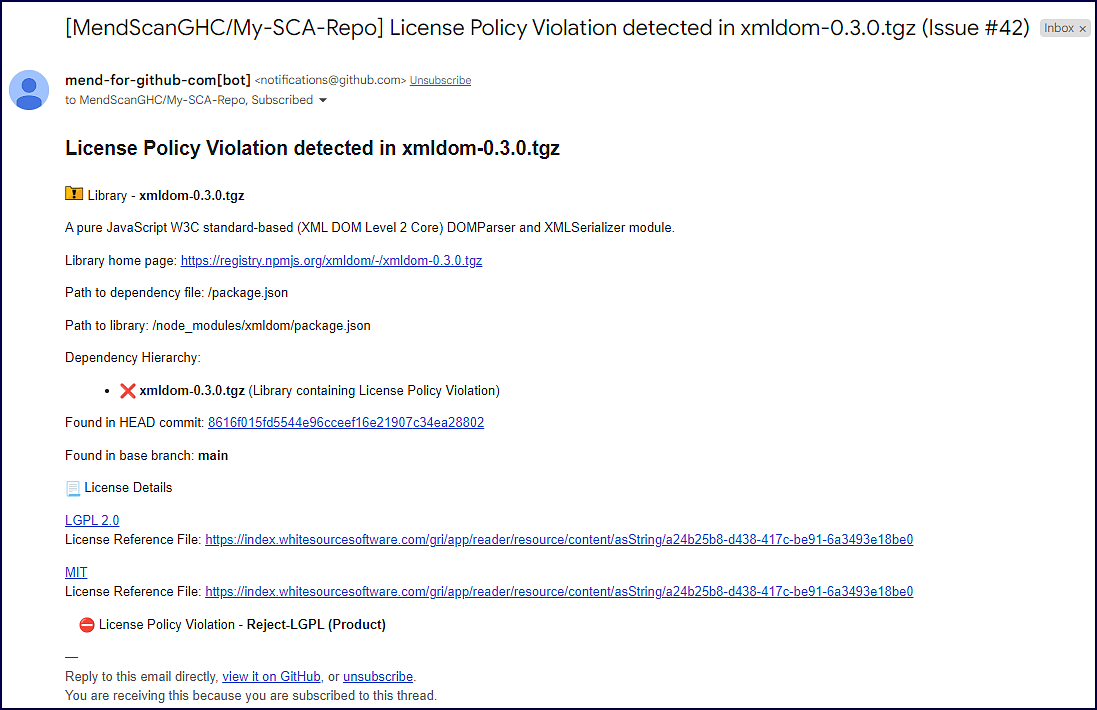
Library: Includes details of the library containing a license policy violation. It also includes the path to the dependency file and the path of the library. If the path is of a transitive dependency, then only the path information of the root library is displayed. This section also contains a commit link, which includes the path to the commit link where the license policy violation was found. NOTE: The originating branch of the license policy violation is also displayed in case the baseBranches configuration was used.
License Details: Description of the license including the license name, a link to the original license, and a license reference file.
Note: When a policy violation affects a library containing multiple licenses, all of the library licenses are displayed, including the license violating the policy.
License Policy Violation: The name of the license policy violation as defined in the Mend SCA UI, along with the policy level (Organization/Product/Project).
Email Notification
Once the Mend for GitHub.com SCA scan is completed, if you have GitHub email notifications enabled for GitHub Issues, you will receive an email for each GitHub Issue created by the SCA scan:
For security vulnerabilities:
For license violations:
GitHub Pull Request
Mend Remediate GitHub Pull Request
Note: By default, Remediate Pull Requests are created with the “security fix” label.
If Remediate is enabled, and remediation is available for an identified open-source vulnerability, a remediate branch called whitesource-remediate/<nameofcomponent>will automatically create a GitHub Pull Request with actions included in the commits to resolve the vulnerability:

Summary:
Package: Name of the open-source component. Includes URL to the vendor and source pages.
Type: Type of Remediate update
Update: Update action
Change: Details on what is being changed
A note is included that links to what GitHub issue will be automatically closed when this Remediate PR is merged.
Vulnerabilities table: Lists the vulnerabilities that will be resolved with the merge of this Remediate PR.
Severity: Level of severity (Critical, High, Medium, Low)
CVSS Score: CVSS score of the vulnerability
CVE: CVE ID of the vulnerability. This links to CVE’s page on Mend’s official database site.
Release Notes: Includes URLs to compare the changes between the versions of the open-source component.
For rebasing/retrying the Remediate PR, select the “If you want to rebase/retry this PR, check this box” option.
Reasons Remediate PR cannot be automatically created despite remediation being available
WHY can this happen? | HOW can a customer fix it? (If applicable) |
|---|---|
No manifest file was found that declares the dependency. (Remediate only makes updates in manifest files, not to a local dependency package file itself) |
|
False Positive / False Negative | N/A; TKA → Mend Squads + Knowledge Team to investigate |
( | Review and edit their configuration as needed. |
There is a severity discrepancy between Issues and PRs configuration. | Review and edit their configuration as needed. |
The dependency package was entirely changed, due to vendor support degradation. (i.e. Ant deprecation) Due to this, updating to the latest version of the “deprecated” dependency may not actually resolve any or all vulnerabilities found. | Research vendor package change and update their project(s) accordingly. |
The dependency is declared in manifest file(s), but no compatabile version is defined. (Renovate doesn’t know what explicit version to start from for updates) |
|
Reasons Remediation isn’t possible for a vulnerability
WHY can this happen? | HOW can a customer fix it? (If applicable) |
|---|---|
A fix version of the dependency doesn’t exist or isn’t available in our database. | N/A; Dependency vendor may not have a fix version released yet For Mend internal: Knowledge Team to investigate validity of adding version to DB. |
False Positive / False Negative | N/A; TKA → Mend Squads + Knowledge Team to investigate. |
The lanaguage/package manager is not supported by Remediate (Supported Package Managers). | N/A; limitation of the product, customer can submit a FR. |
The dependency package was entirely changed, due to vendor support degradation. (i.e. Ant deprecation). Due to this, updating to the latest version of the “deprecated” dependency will not resolve any of the identified vulnerabilities. | Research vendor package change and update their project(s) accordingly. |