Using Mend for GitLab
Initiating a Scan
A Mend scan is initiated via a valid GitLab push command. A valid push command meets at least one of the following requirements:
One of the commits in the push command added/removed a source file(s) that has an extension supported by mend.
Refer to the Mend Languages page to find out whether or not a specific language and its extensions are supported.One of the commits in the push command includes an addition/modification of the package manager dependency file(s).
Refer to the list of supported dependency files to find out whether your dependency files are supported.
Note: a push command may consist of multiple commits.
Note: For a Conan dependencies scan, the SCA orchestrator scanner environment variable must be enabled (MEND_SCA_ORCHESTRATOR_ENABLED=true).
Inventory post-scan
Mend continuously researches new vulnerabilities and updates its vulnerability database with these findings. For these newly discovered vulnerabilities to be reflected in projects as soon as possible, Mend initiates a post-scan process for all integrated projects every 6 hours and additionally at 01:00 UTC. Mend will create or update issues and pull requests for vulnerabilities that were added to the database during this period.
This is an automated procedure, and no action from the user is required.
Viewing Details of the Scan
Results can be viewed in the following places:
The Issues tab within the GitLab project.
The Mend Security/License Check within the GitLab project's Commits tab.
The Mend UI.
Via email notifications.
For GitLab Ultimate users:
The GitLab security dashboard
Pipeline reports
Viewing the Issues Tab
If you are performing Merge Requests or push commands via the Web browser, refresh your Web browser to view the issues that were generated by mend. NOTE: It may take several minutes for the issues to be scanned and displayed after a valid push command is initiated.
The Issues tab displays all the issues that the Mend Integration detected with the red Mend: dependency security vulnerability label. This proprietary label indicates a security vulnerability was detected by mend.
As part of your workflow, you have the option to add a relevant label(s) to specific issues, and close issues that were resolved.
Issues that were manually closed will not be re-opened during future Mend scans unless their label and/or name have been manually changed or changed via the GitLab API.
Viewing Details of an Issue
See here for more information.
Viewing Mend Security Checks
Commit Status indicators are displayed for each head commit on the Commits sub-tab of the Project tab.

NOTE: The commit statuses above are the red X and the green check mark.
Clicking a specific indicator will redirect you to the relevant Commit page, where you can find the Mend Security Check for the selected head commit in the Changes sub-tab, which contains a security report.
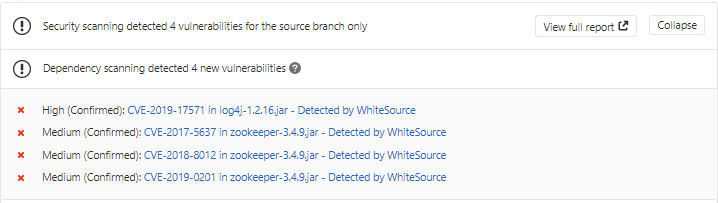
The security report displays all the vulnerabilities that were found in descending order according to the severity and CVSS score. The following information is displayed for each vulnerability:
CVE: A link to the related CVE page for the vulnerability. Displayed in a collapsible format (click the arrow to expand/collapse for more information regarding the vulnerability).
Severity: Overall score of the severity (High, Medium or Low).
CVSS Score
Vulnerable Library
Suggested Fix
Issue: A link to the Mend issue that was generated for the vulnerability.
Types of Indicators
The following commit status indicators are available as feedback on the head commits:
Pending: The Mend scan has not begun and is scheduled to begin.
Running: The Mend scan is in progress.
Neutral: The Mend scan did not run because a valid scan initiation action did not occur.
Success: The Mend scan was completed successfully and no vulnerabilities were detected.
Failed: The Mend scan did not complete successfully, this is the default for all completed scans. NOTE: a failed status may be shown due to security vulnerabilities, or due to an error that occurred during the scan.
Note: Mend Security Checks in non-base branches that would have been considered a Neutral check will instead always have a Failed status if the previous check failed. For example:
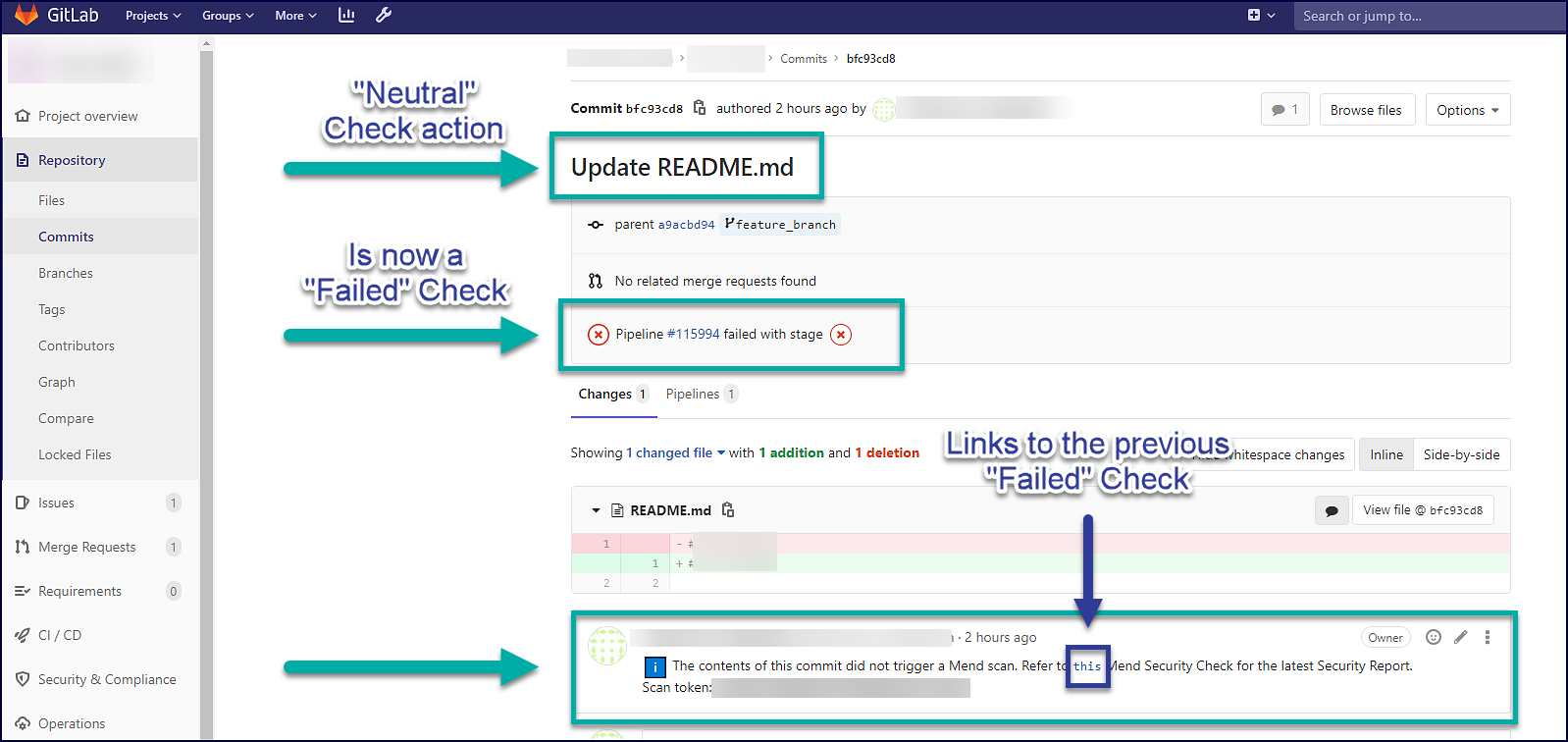
Samples of Commit Status Indicators
Running
The following is a sample of a Running status, which indicates that the security check is currently scanning the head commit.

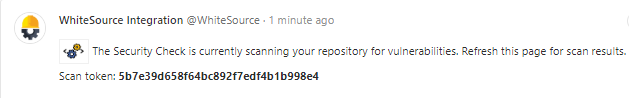
Success
When no vulnerabilities are found and no errors occur during the scan, Mend will display the following commit status, and a security report indicating that no vulnerabilities were detected:

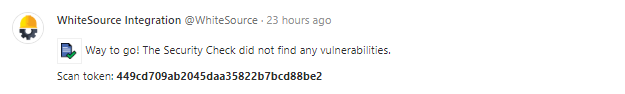
Failed
All head commits that fail the scan due to the security check detecting vulnerabilities or due to an error that occurred during the scan will display a failed commit status.
The following screenshot displays a failure indicator for a head commit

Security Check with Partial Scan results
In case when during the scanning of the repository Mend encountered exceptions thrown by the package managers there will be a message indicating that the scan results might be partial (i.e. Mend was not able to pull all of the dependencies for scanning).
This message is displayed only in the description of the Security Check and does not affect its status. It is also possible to use the strictMode parameter so all the Checks with this message will fail even if no vulnerabilities are detected during the scan.
Viewing Mend License Checks
In the Commits tab, you can view the status and results of each scan. Click a specific build icon to view the Builds page.
Types of Indicators
The following commit status indicators are available as feedback on the head commits:
Success: No license policy violations were detected.
Failed: One or more license policy violations were detected during the Mend scan.
Viewing Details in the Mend UI
In the Mend UI, Mend projects will have the same name as the corresponding GitLab repository, with a "GL_" prefix, unless otherwise specified in the. Mend file using a project token.
The name of the Mend product will be the same as that of the GitLab group preceded by a "GL_" prefix if the GitLab project is under a group. Otherwise, the name will be your GitLab username preceded by "GL_".
Viewing the Security Dashboard
GitLab Ultimate users have access to GitLab’s security dashboard.
Vulnerabilities detected by Mend for GitLab can be identified by their “ - Detected by Mend” suffix.
Viewing Details of a Vulnerability in the Security Dashboard
Description: A description of the vulnerability.
Project: The GitLab project the vulnerability exists in.
File: The manifest file the vulnerable dependency is declared in.
Identifiers: The original identifier of the vulnerability.
Severity: The vulnerability’s severity. Possible values are:
High
Medium
Low
Confidence: How reliable this vulnerability assessment is.
Vulnerabilities detected by Mend will always have “Confirmed” confidence.
Report Type: The security report this vulnerability belongs to (dependency_scanning, etc.).
Vulnerabilities detected by Mend will always have the “dependency_scanning” report type.
Links: Any references to external documentation pieces or articles that describe the vulnerability further.
Solution: An explanation of how to fix the vulnerability.
Viewing the Pipeline Reports
Pipeline reports can be viewed from the following places:
Within the CI/CD pipeline by clicking CI/CD > Pipelines > Pipeline # > Security.
Within MRs from feature branches to the main branch by clicking Expand in the Security Scanning section of the MR.