API 3.0 - Use with Postman
Overview
The easiest way to get started with Mend API 3.0 is to use it inside an API platform tool like Postman.
Mend Tip: We recommend reading our Getting Started with Mend API 3.0 documentation to understand the API’s basic functionality before diving into this implementation article.
Getting it done
Prerequisites before using the Mend Container Image API in Postman
Copy and save Mend API 3.0 locally in a JSON-formatted file
Configure the Mend API 3.0 in Postman
Step One: Import the Mend API 3.0 as a Postman Collection
Download the API’s definition in JSON format, by accessing the API 3.0 documentation and clicking the Download button.
This opens a browser tab containing the API definition in JSON format.
Select all the text (in JSON format) and copy.
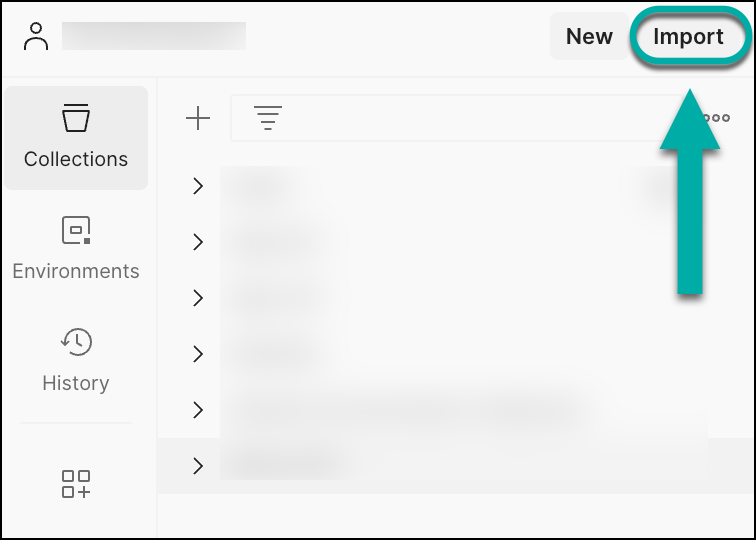
Open your Postman instance.
Select Import.
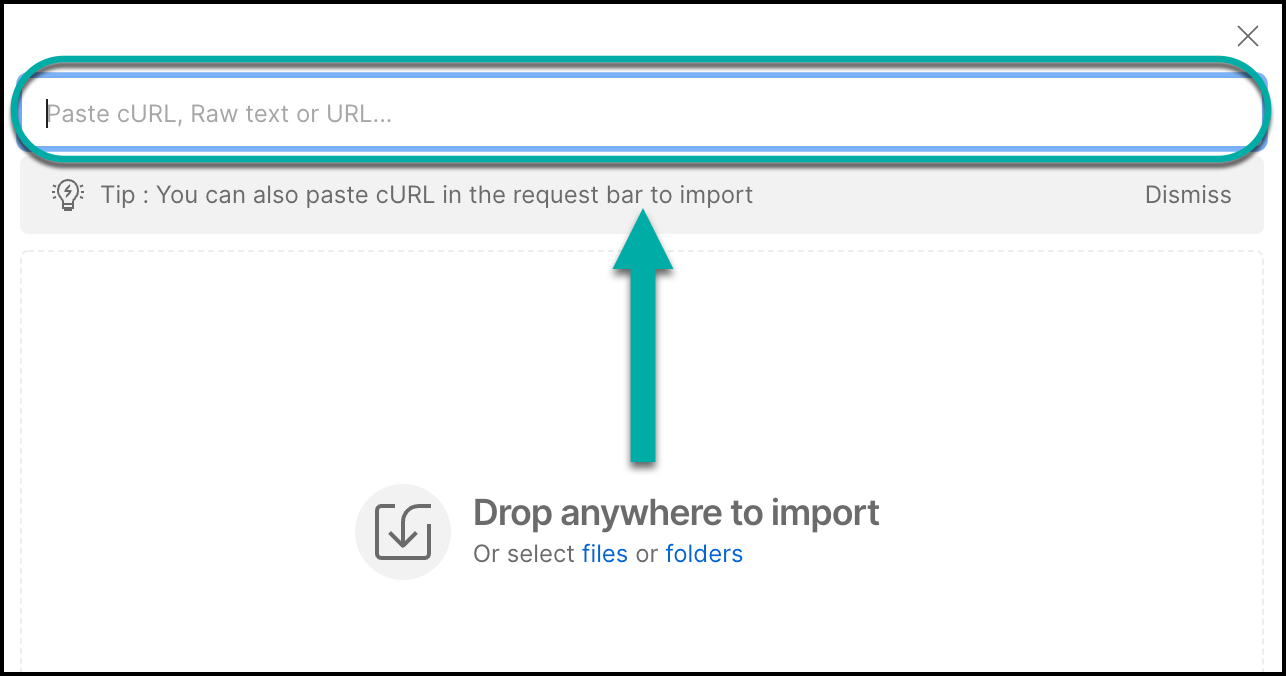
A new window will pop up. Paste the definition into Postman:
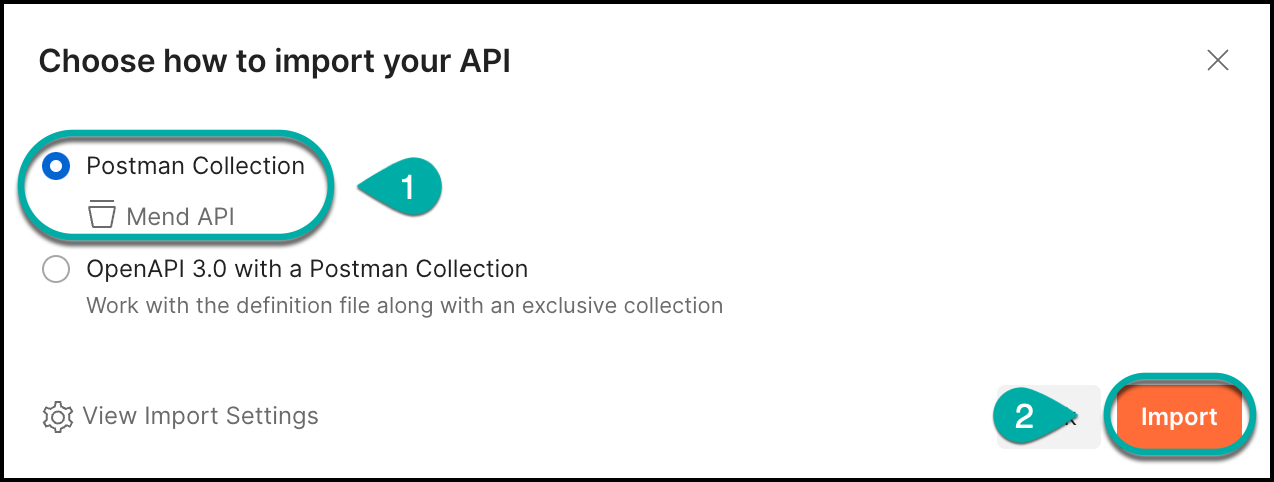
Select Postman Collection, then click on Import:
Copy your base URL, depending on your Mend Platform environment. The format of the URL is:
For Mend instances:
https://api-<instance>.mend.io/api/v3.0For WhiteSource instances:
https://api-<instance>.whitesourcesoftware.com/api/v3.0
Examples: https://api-saas-eu.mend.io/api/v3.0 | https://api-saas-eu.whitesourcesoftware.com/api/v3.0
Insert this URL as the
{{baseUrl}}environment variable in Postman. You can set this in your Collection-level variables, Globals, or use a separate, dedicated environment for the Mend API and create the{{baseUrl}}environment variable there: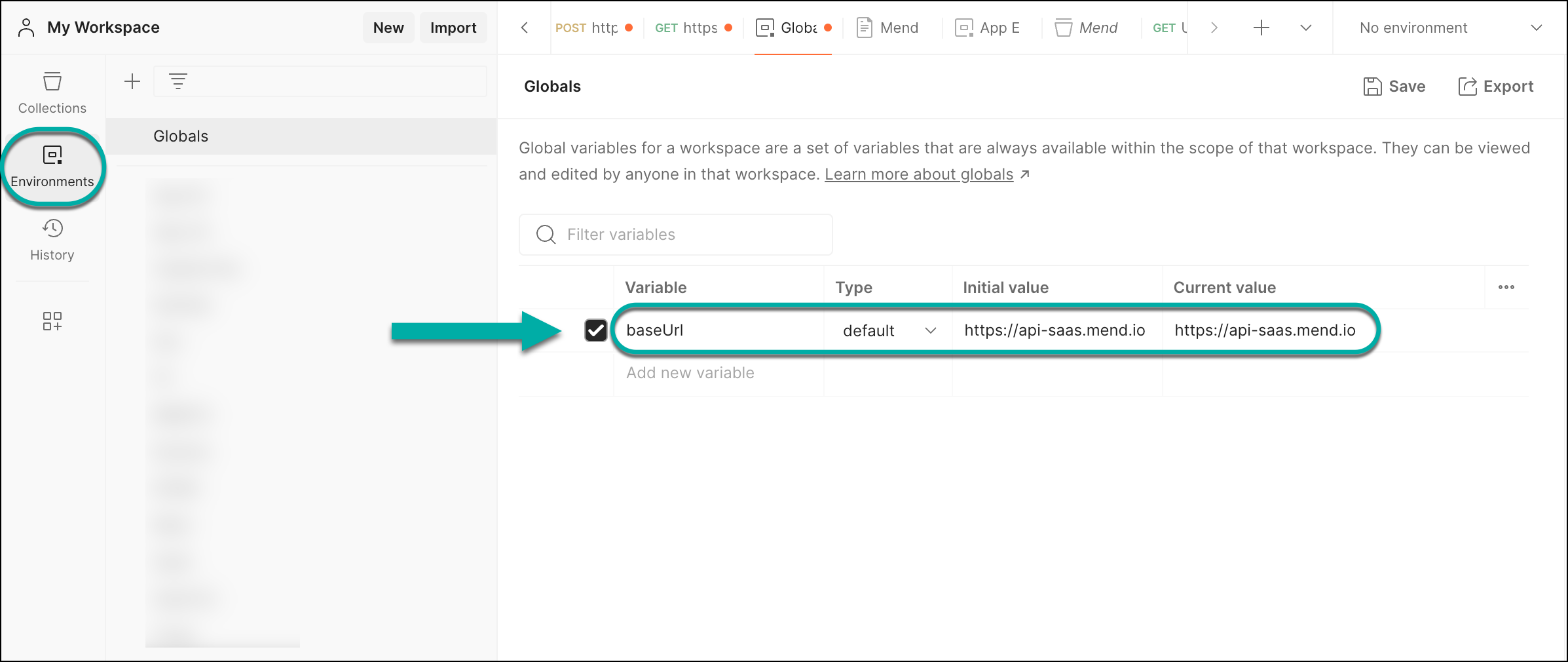
Log into Mend API 3.0
You must have a valid Mend user to log in to an organization to use the API endpoints. Use the login endpoint and add the following:
Your email address associated with your Mend user (Mend Platform → My Profile → General)
Your organization UUID (Mend Platform → Administration → General Configuration → Organization UUID)
Your Mend user key (Mend Platform → My Profile → User Keys)
Tip: Set the credentials above for the login endpoint using Postman environment variables. For example:
{
"email": "{{email}}",
"orgUuid": "{{orgUuid}}",
"userKey": "{{userKey}}"
}The response returns the orgUuid and a refreshToken which is valid until it expires (30 minutes), for that organization only.
Note: Once logged in, you should log out before accessing a different organization.
Retrieve a jwtToken
Open the Refresh Access Token endpoint. Create a header key called wss-refresh-token and insert the refreshToken from the previous step:
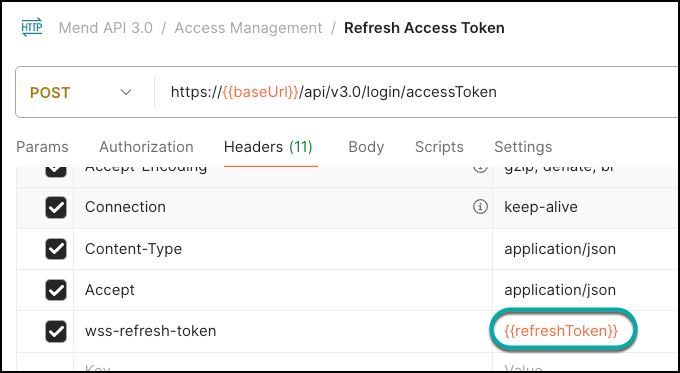
Calling this endpoint returns a jwtToken that is used to authenticate further API requests.
Authenticate Mend API 3.0 Calls in Postman
You will need to use the jwtToken to authenticate the API call for the specific organization. Each API call may require certain path variables, such as orgUuid or userUuid, depending on things such as the hierarchy level, report configuration requirements, etc.
Let’s use the Get Project Libraries (Dependencies - SCA) call as an example. To add the jwtToken to the call in Postman:
Select the Authorization tab and select Bearer Token.
Place the
jwtTokenvalue provided earlier into the Token setting: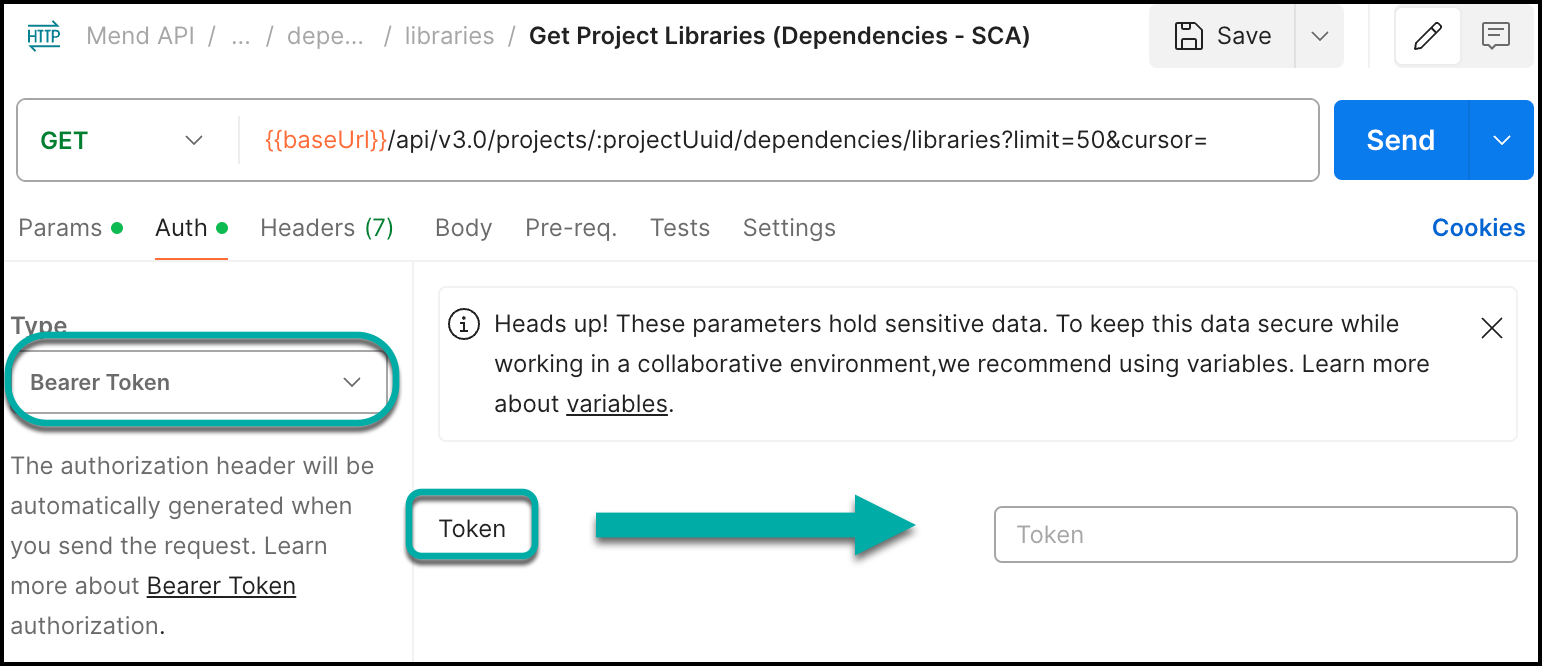
Save your changes.
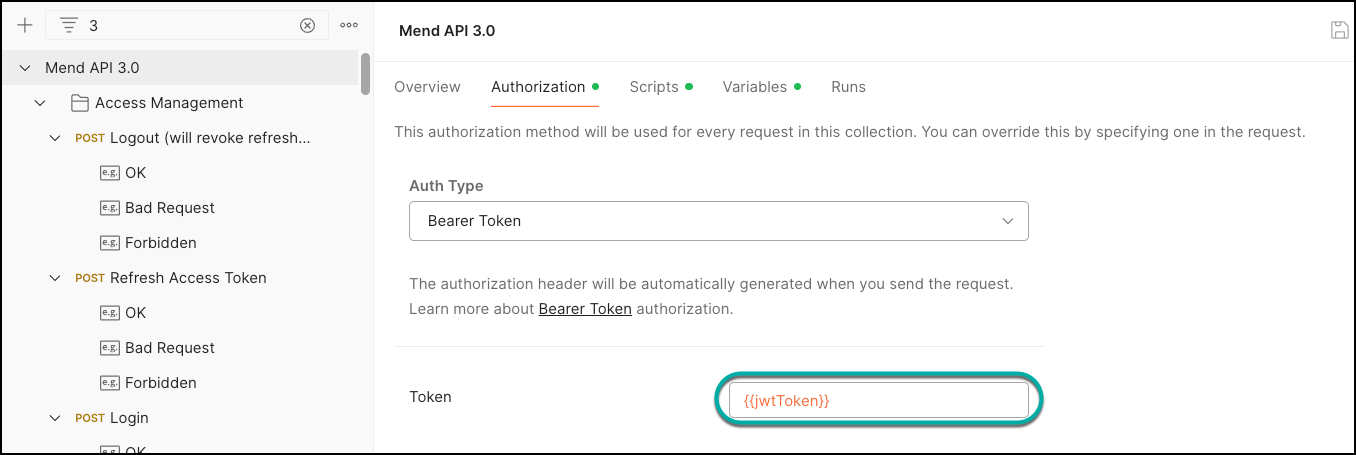
Tip: For step 2, you can keep the Authorization Type as “Inherit auth from parent” and insert the jwtToken as a Postman environment variable for the API 3.0 collection:
Continuing with our Get Project Libraries (Dependencies - SCA) call example, you will also need to set your projectUuid in the Path Variables. To do so:
Select the Params tab.
Under Path Variables, find the projectUuid Key and input your
projectUuidreceived during login into the Value setting (Note: You can also set this as an environment variable):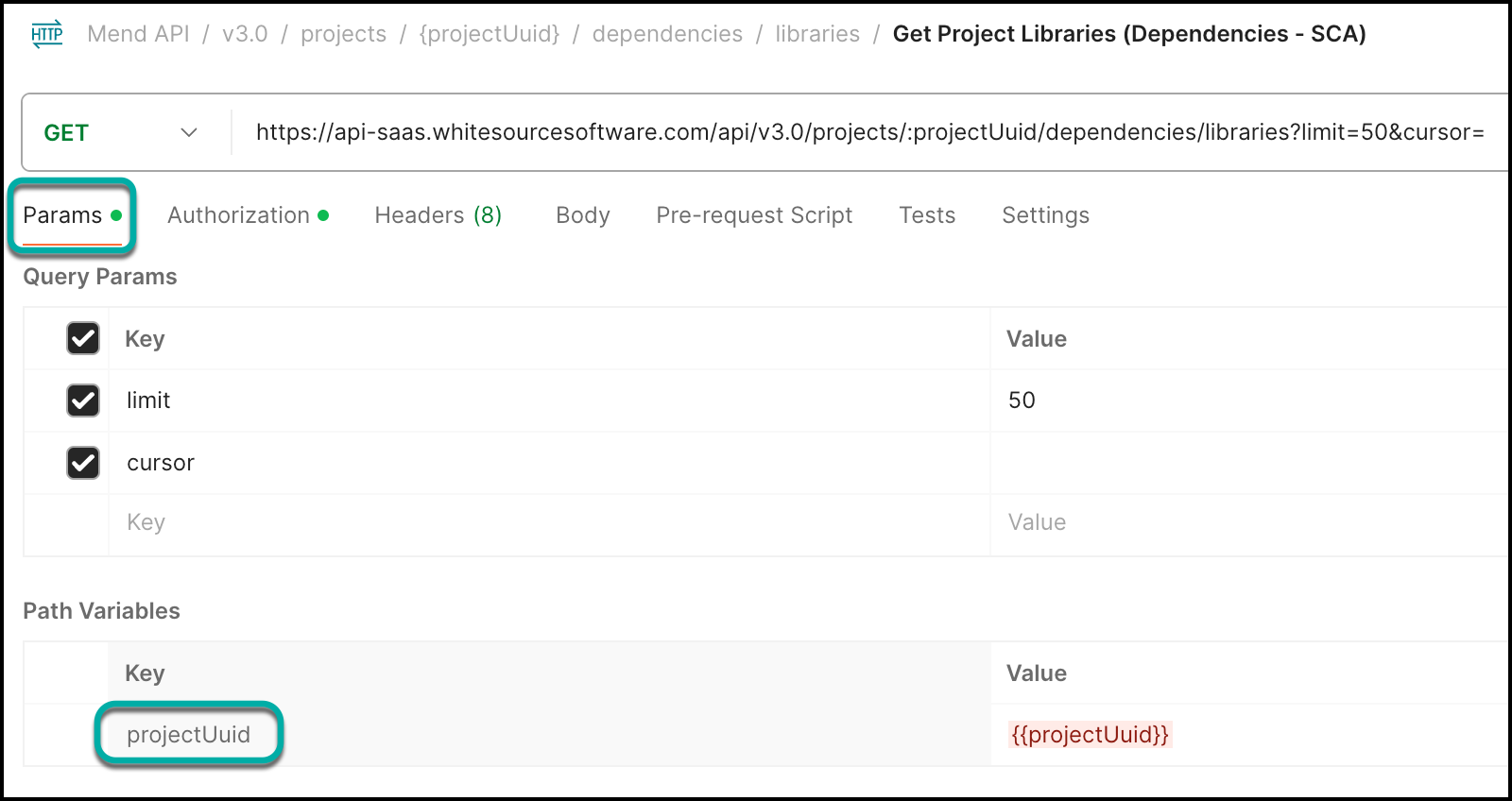
Save your changes.
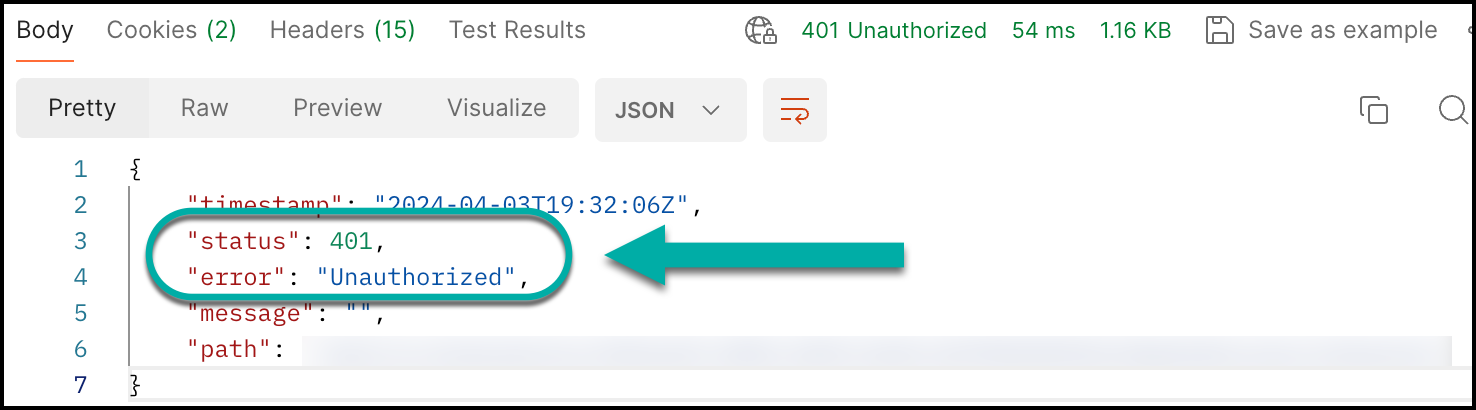
Note: If you get Error 401 Unauthorized, it's because you forgot to add the bearer token or are accessing the wrong organization.
Pagination and Sorting for Large Results
For large results, the API’s scalability allows:
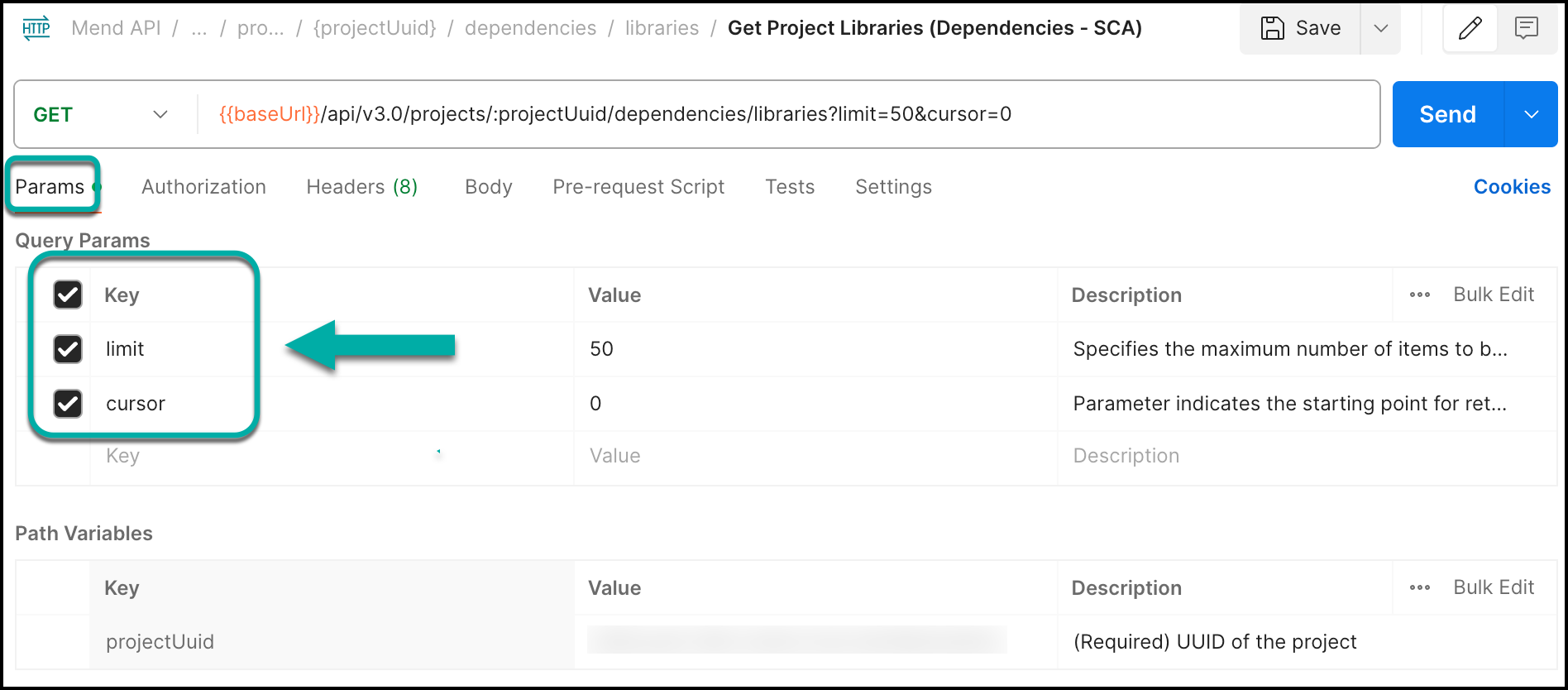
Limit by default is 50 results, where the first page is page 0. You can change the size of the page by editing
limitwhile the maximum value forlimitis 10,000.Cursor indicates the starting point for retrieving results, the first call doesn't include a cursor parameter in the request, the API response includes the first set of results along with a cursor pointing to the last item retrieved.
