Malicious Packages in Mend SCA
Overview
Mend SCA detects malicious packages in your projects and provides detailed information about the threats that they carry. Malicious packages must be removed immediately as they contain functionality that actively seeks to undermine, steal data, or inject malicious code into your app.
Getting it done
Detect Malicious Packages
Malicious package detection is now automatically integrated into Mend SCA scans. Findings are reported in the Mend AppSec Platform UI.
Step 1 - Navigate to the Dependencies page of your application
Step 2 - You will see the Malicious icon (![]() ) under the Risk Factors column (you can use the filter to list only Malicious packages).
) under the Risk Factors column (you can use the filter to list only Malicious packages).
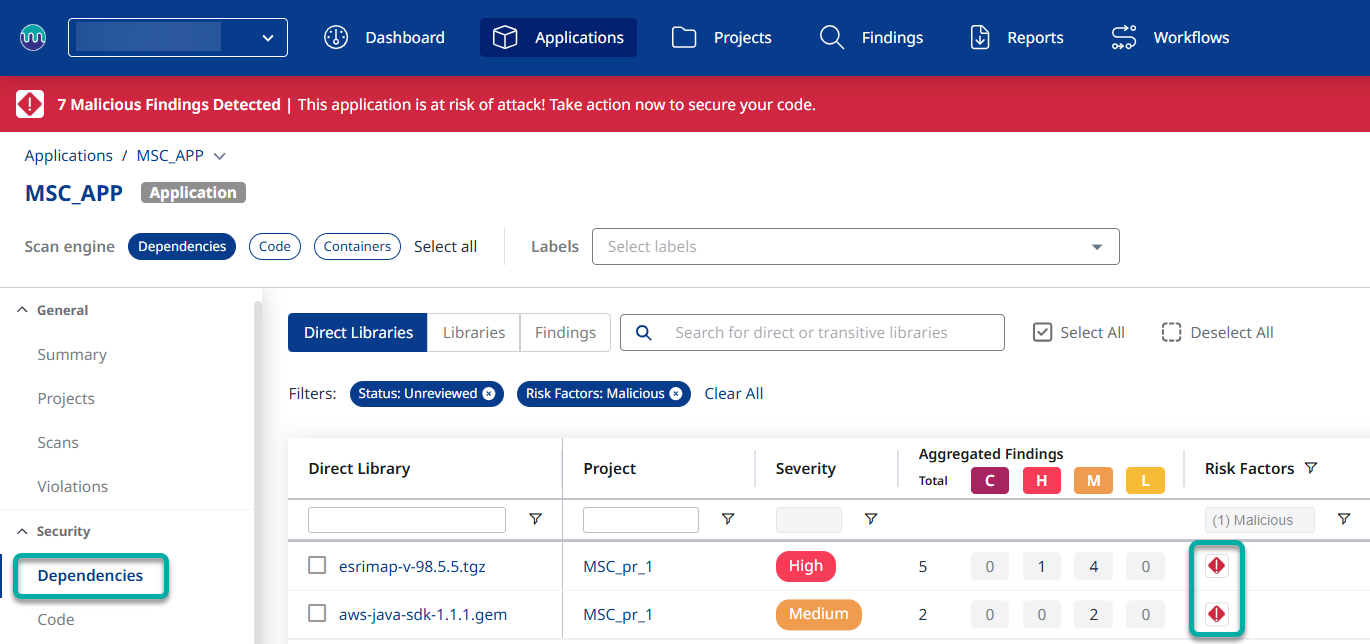
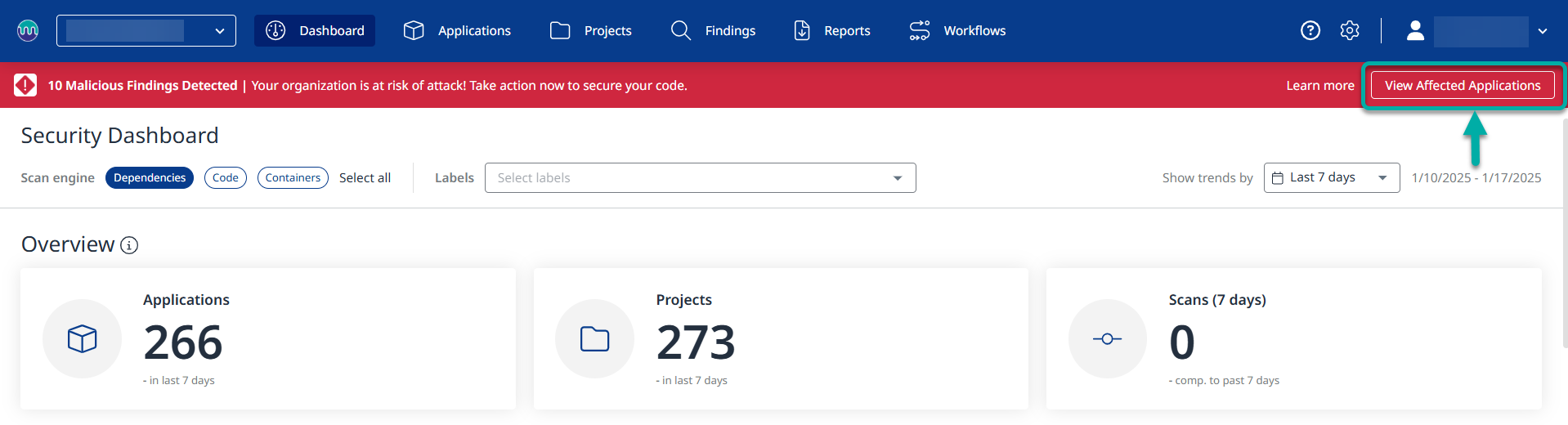
Note: The existence of malicious packages in your application/project usually calls for immediate action. For this reason, as you access an impacted organization, a warning banner will be displayed at the top, allowing you to view affected applications with a click of a button:
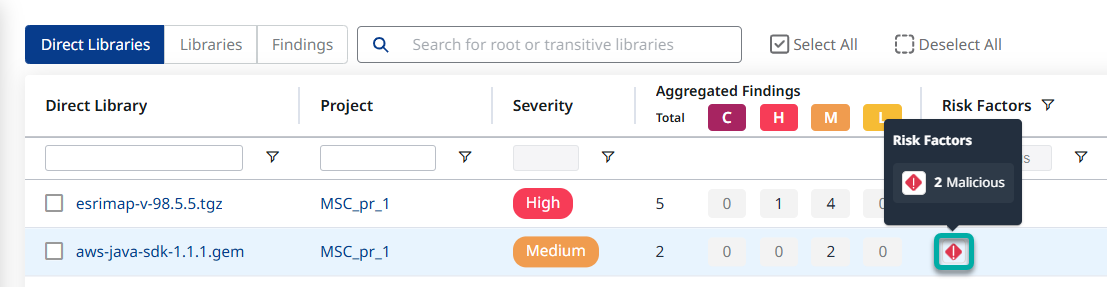
Step 3 - Hovering over the Malicious icon on the Risk Factors column will show you how many malicious vulnerabilities (MSCs) impact the package in question.
Step 4 - Clicking the icon will take you to the Vulnerabilities page, where additional information about the vulnerabilities can be reviewed.
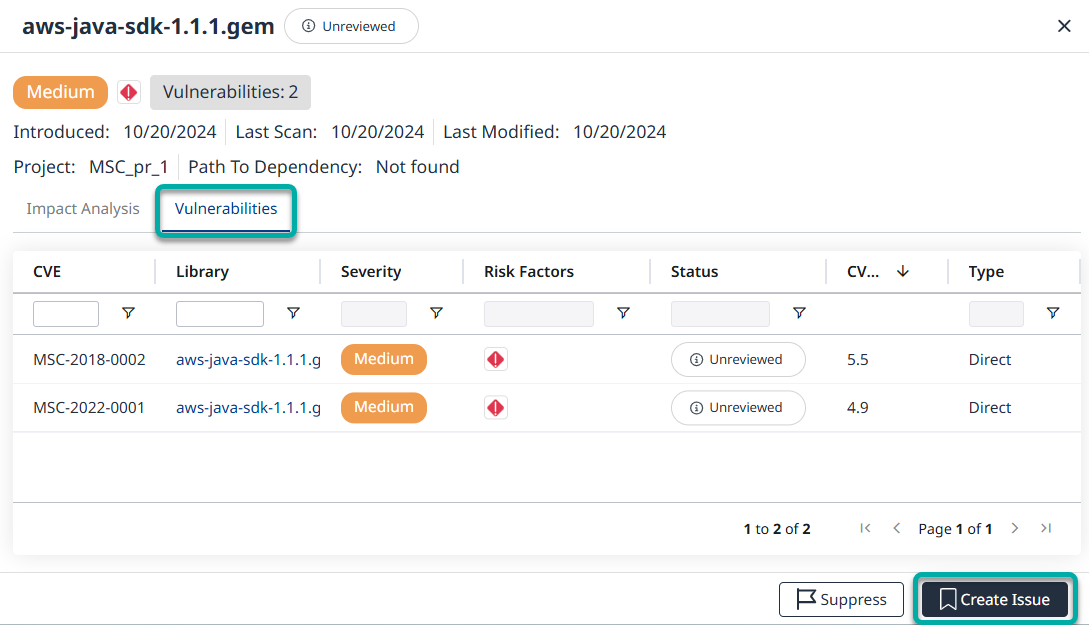
Note: At this stage, assuming you have an Issue Tracker integration in place (e.g., Jira), you can create an issue for your development teams to take further action.
Remove a Malicious Package
In general, there are no remedies for malicious packages. Upgrading to a newer version is not likely to help since the risk usually persists. Downgrading to an older, unaffected package is an option, but the best solution is to remove the package from your project and find a different one to use instead.
However, there are some things to check. Look at the name and the version of the package carefully, they may have been changed slightly from the original to confuse you. Check that you downloaded the package from a reputable source, and check online forums for more information. Notify the registry managers (e.g., npm, PyPI) about the package.
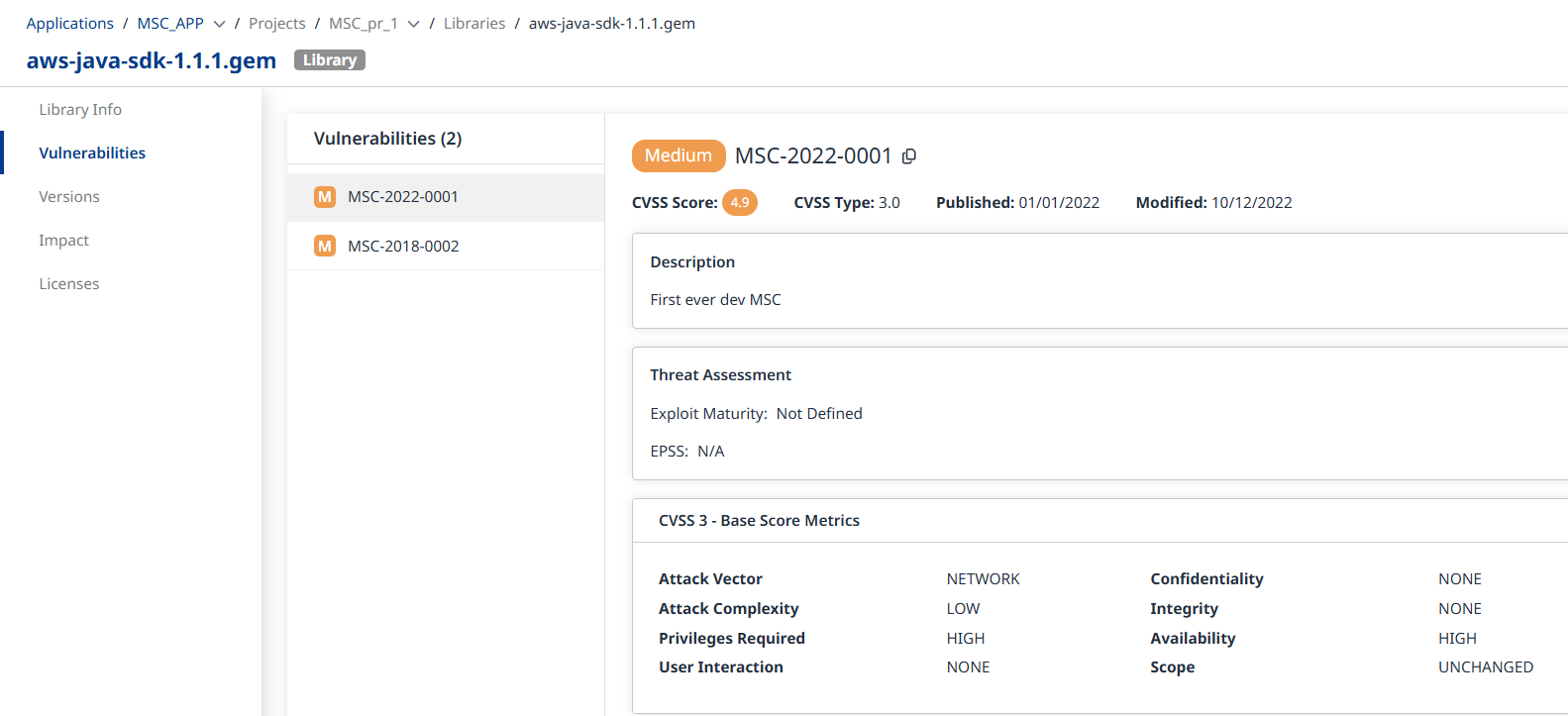
Click on the library to be taken to the Vulnerabilities section of the library information, where you can review the details of each vulnerability, including CVSS metrics:
Reference
Mend.io employs unique methods for malicious package detection that delivers accurate results with very few false-positives. It checks many parameters besides library signatures to determine if a package poses a risk. Mend.io’s security research team further augments the automated analysis for even greater accuracy.
Here are some malicious package types that may be encountered:
Protestware
This type of malware promotes a particular political or social cause. Its goal is to display images and messages related to the cause, and in some cases it may perform malicious actions like deleting files, altering data, or disrupting the normal operation of a system.
Info Stealers
Information-stealing malware gathers valuable information from infected systems which can then be used for various malicious purposes, such as identity theft, financial fraud, corporate espionage, or further cyberattacks. Info stealers use various techniques to obtain sensitive data, including keylogging, clipboard monitoring, browser data extraction, screen capturing, memory scraping, and much more.
Crypto Miners
These programs are designed to mine cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, Bonero and Ethereum, on the victim’s machine without the target’s consent. Miners generate revenue for the attacker by utilizing the target’s computer resources, leading to performance degradation. Miners are stealthy and so hard to detect, and they persist even after restarting or shutting down the machine.
Obfuscation code
Obfuscated code replaces an application’s code and it has been intentionally altered to make it difficult for humans or automated tools to detect. Obfuscation techniques are often employed by attackers to hide the presence of active malicious code and bypass security measures.
Common obfuscation techniques include variable and function renaming, control flow obfuscation, string obfuscation, code packing, dead code insertion and ‘opaque predicates’.
Remote Reverse Shells
This malicious software establishes a connection between an infected system and an attacker's machine, providing the attacker unauthorized access and control over the target system, opening it to data theft, system reconnaissance, entry to the network and deploying additional malware.
Malware dropper
Cybercriminals often use droppers to bypass security measures and avoid detection by antivirus apps since they are disguised as legitimate or innocuous files. Their primary purpose is to deliver and install other malware components onto a target system.
Recommendations
Make sure that the package was downloaded from a reputable registry.
Packages containing spam or protestware are not considered harmful, although they do signal that someone with malicious intent has their eyes on the package.
If the package is a popular one (say, with more than 10k downloads), than this is likely an isolated “account takeover” incident and it may then be possible to downgrade or upgrade the package version.
Mend recommends contacting your security department immediately so that they can take further action such as:
Reviewing logs and other system data to determine if the package has compromised any sensitive information or caused other damage.
Disconnecting the affected system from the network to prevent further data exfiltration or spread of the malicious package.
Limiting access to the affected environment to essential personnel.
Remember, malicious packages are nothing like regular open-source vulnerabilities (CVEs). Vulnerabilities represent a potential threat to your environment, whereas malicious packages must be treated as active cyber attacks.
Supported threat types
The following threats are detected by Mend CLI:
Data exfiltration
Spam packages
Protestware
Info stealers
Crypto miners
Obfuscation code
Remote reverse shells
Malware dropper
Malicious Packages (MSC) - Supported Registries
Below is a table of registries supported for the detection of malicious packages.
